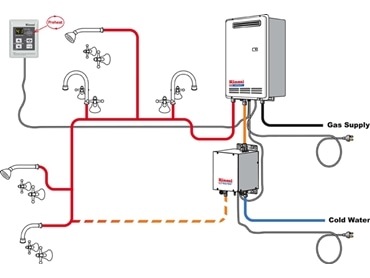
Gas hot water systems heat water using a gas burner. Cold water enters the system, where a gas burner heats it inside a storage tank or a heat exchanger for continuous flow models. A thermostat regulates temperature, and exhaust gases vent through a flue. These systems provide efficient and fast water heating.
The Detail – How Gas Hot Water Systems Work
A gas hot water system uses natural gas or propane to heat water for household use. The process begins when cold water enters the unit through a dip tube (in storage models) or passes through a heat exchanger (in continuous flow models). The gas burner ignites, generating hot air that transfers heat to the water. A thermostat regulates water temperature, while a pressure relief valve ensures safety.
Gas Hot Water System Heating Process
Water Entry – Cold water enters through the dip tube or water inlet.
Gas Ignition – The gas burner ignites, heating the secondary heat exchanger in some models.
Water Heating – Heat transfers to the water via the heat exchanger.
Temperature Control – The thermostat adjusts gas flow to maintain set temperature.
Hot Water Delivery – Heated water flows to the hot water tap when needed.
Key Components of a Gas Hot Water System
Each gas water heater includes essential parts for energy efficiency and reliable performance.
Component | Function |
|---|---|
Gas Burner | Ignites natural gas or propane to heat water. |
Heat Exchanger | Transfers heat to flowing water in continuous flow models. |
Water Tank | Stores hot water in storage systems. |
Dip Tube | Directs cold water to the bottom of the gas hot water tank. |
Thermostat | Controls water temperature by adjusting gas flow. |
Pressure Relief Valve | Prevents excessive water pressure buildup. |
Anode Rod | Reduces corrosion inside gas storage HWS tanks. |
Gas Control Valve | Manages gas flow for temperature control. |
Flue Pipe | Vents burner exhaust gases safely outdoors. |
Electronic Control Unit | Regulates ignition, safety features, and automatic gas cut-off. |
Flow Sensor | Detects flowing water and activates the instant gas HWS burner. |
Types of Gas Hot Water Systems
Gas hot water systems are available in storage tank and instant gas HWS (tankless) models.
Storage Gas Hot Water System (Gas Storage HWS)
Stores preheated hot water in a gas hot water tank.
Heats continuously to maintain a ready supply.
Suitable for high-demand households.
Continuous Flow (Tankless) Gas Hot Water System
Heats cold water on demand using a heat exchanger.
Provides continuous hot water without storage losses.
More energy efficient, reducing cost savings.
Image: a continous flow gas hot water system
Gas Boosted Solar Hot Water Systems
Uses solar hot water systems as a primary source.
The gas burner activates when solar heating is insufficient.
Provides greater energy efficiency and a lower carbon footprint.
Energy Efficiency and Running Costs
Gas water heaters have higher energy efficiency than electric models due to the faster heating process and lower operational costs.
Factors Affecting Energy Rating and Cost Savings
System Type – Continuous flow models are more energy efficient than storage systems.
Gas Connection Installed – Homes with an existing gas line avoid additional setup costs.
Energy Rating – Higher-rated models consume less natural gas, reducing bills.
Water Usage – Efficient use of hot water taps minimizes waste.
Insulation – Well-insulated storage tanks retain heat longer.
Gas Hot Water Safety Features
Safety mechanisms ensure gas hot water systems operate reliably and prevent hazards.
Essential Safety Features
Pressure Relief Valve – Releases excess water pressure to prevent explosions.
Flame Sensor – Detects if the gas burner is lit and stops gas flow if unlit.
Carbon Monoxide Venting – Flue pipes remove dangerous burner exhaust gases.
Automatic Gas Cut-Off – Stops gas flow if the electronic control unit detects a fault.
Gas Pipes & Venting – Ensures proper gas connection and exhaust management.
Troubleshooting Common Gas Water Heater Issues
Pilot Light Not Staying Lit
Possible gas valve or flame sensor issue.
Ensure proper gas flow and clean burner components.
Water Not Heating Properly
Check thermostat settings and gas burner operation.
Inspect for sediment buildup in the gas hot water tank.
Strange Noises
Sediment accumulation in storage tanks may cause rumbling.
Gas pipes may need adjusting for proper gas flow.
Gas Smell or Leaks
Turn off the gas connection immediately.
Contact a licensed technician for gas line inspection.
Maintenance Tips for Greater Energy Efficiency
Regular maintenance improves energy efficiency and extends system lifespan.
Gas Hot Water System Maintenance Checklist
✅ Flush the Tank – Remove sediment buildup in storage systems every 6-12 months.
✅ Check the Anode Rod – Replace every 3-5 years to prevent corrosion.
✅ Inspect Gas Pipes – Ensure no leaks in the gas connection installed.
✅ Adjust Thermostat – Set between 120-140°F for cost savings and safety.
✅ Test the Pressure Relief Valve – Prevent excessive water pressure damage.
Popular Questions
Below are common questions we get asked about this topic.
Can I install a gas hot water system in a high-rise apartment?
Installing a gas hot water system in a high-rise requires proper ventilation. Continuous flow models are preferred due to compact design and minimal exhaust requirements. Gas connection availability is a key factor.
How does altitude affect gas water heaters?
Higher altitudes reduce oxygen levels, affecting gas burner combustion. Some models require high-altitude kits for optimal performance above 2,000 feet.
Can I use a gas water heater with solar panels?
Yes, solar hot water systems can integrate with gas storage HWS as a backup heat source, improving energy efficiency and cost savings.
Do gas hot water systems work during power outages?
Some gas water heaters function during a power outage if they use a standing pilot light. Electronic control unit models require backup power or batteries.
Gas hot water systems provide instant hot water, energy efficiency, and cost savings. Choosing the right system depends on household demand, gas connection, and budget. Regular maintenance and greater energy efficiency features enhance system performance while ensuring safety and reliability.